3D Scanning
The specifications of a 3D scanner are essential in determining the accuracy, detail, and quality of the 3D model it generates. A high-quality scanner is crucial for ensuring the modeling process yields reliable, precise, and usable results. Here’s a closer look at the specifications that define a great 3D scanner and why they are important:
Resolution
Higher resolution means more data points are captured, resulting in finer detail and a higher-quality mesh. It’s essential for accurately modeling intricate objects but can increase scan time.
Accuracy
Accuracy ensures the digital model closely matches the real-world object, making it crucial for precise applications. High accuracy is particularly important in industries like engineering and healthcare to minimize measurement errors.
Scan Volume
Scan volume determines the size of the area the scanner can capture in a single pass, impacting its versatility. A larger field of view is useful for big objects, while a smaller volume is better suited for detailed scans of smaller items.
Scanning Speed
Faster scanning can improve workflow efficiency, especially in high-volume or time-sensitive projects. However, some high-speed scanners may compromise on detail, so balancing speed and quality is important.
Texture Capture (Color Scanning)
Texture capture adds realism by recording color and surface details, which enhances the model’s visual accuracy. It’s valuable for fields like gaming, product design, and marketing that require detailed appearances.

Resolution
Definition: In 3D Scanning the resolution refers to how closely the scanner can capture data points. It is often measured in points per square inch or the number of data points (point clouds) collected per scan.
Importance: A higher resolution scanner can capture more detail, resulting in a finer mesh with greater accuracy. For applications like reverse engineering, capturing intricate details of mechanical parts, or scanning small objects, a high-resolution scanner is critical. Low resolution can result in blurry or inaccurate models that need extensive cleanup.
Accuracy
Definition: Accuracy refers to how closely the scanned data matches the actual physical object. This is usually measured in millimeters or microns (μm).
Importance: High accuracy ensures that the digital model represents the real-world object faithfully. In industries like healthcare (e.g., prosthetics) or aerospace (e.g., components), even small inaccuracies can lead to significant functional issues. A great scanner ensures that measurements are as precise as possible, reducing errors in the final model.

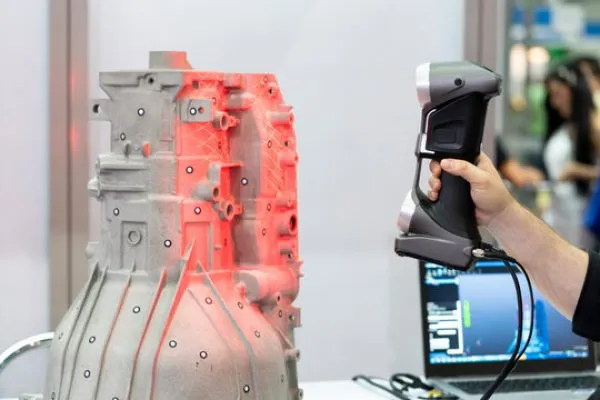
Scan Volume
Definition: The scan volume is the size of the area or object that the scanner can capture in a single scan. This can range from small objects (a few centimeters) to large-scale objects (several meters).
Importance: A scanner with a large field of view is ideal for scanning bigger objects like vehicles, buildings, or machinery, without the need for multiple scans. On the other hand, for small, intricate items, a scanner with a smaller, more focused field of view provides higher resolution and more detail.
Scanning Speed
Definition: Scanning speed refers to how quickly the scanner can capture the data needed for a 3D model.
Importance: A faster scanning process is crucial for time-sensitive projects or mass scanning tasks. For example, in manufacturing or production environments where prototypes need to be generated quickly, a high-speed scanner can significantly improve workflow efficiency. However, speed should not come at the cost of resolution or accuracy.
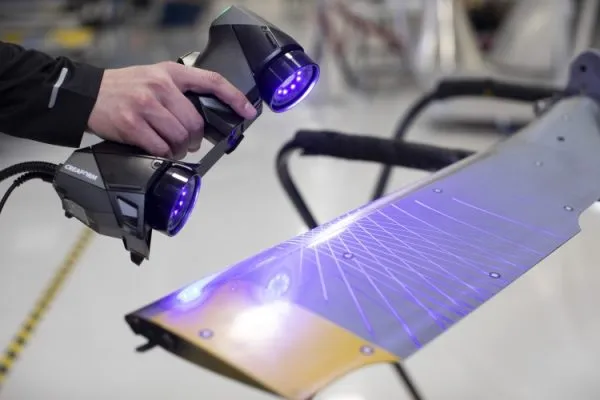
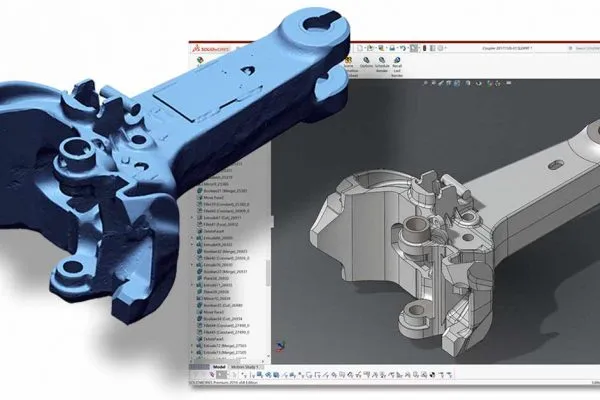

Texture Capture (Color Scanning)
Definition: Some 3D scanners are equipped with the ability to capture color or texture data, which adds surface details like color, patterns, and texture to the 3D model.
Importance: For realistic models used in animation, gaming, or virtual reality, texture capture is essential to produce visually accurate results. This is also important in industries like fashion or product design, where the visual appearance and texture of the model matter greatly.
Contact Us Today
Contact us today to discuss your 3D scanning needs and learn how we can bring your ideas to life. Our dedicated team is ready to provide expert guidance and support, ensuring a smooth experience every step of the way.
Nashville, Tennessee, USA | Phone: 800-453-3801 | Email: info@zagnat.com
Copyright © 2025 Zagnat
